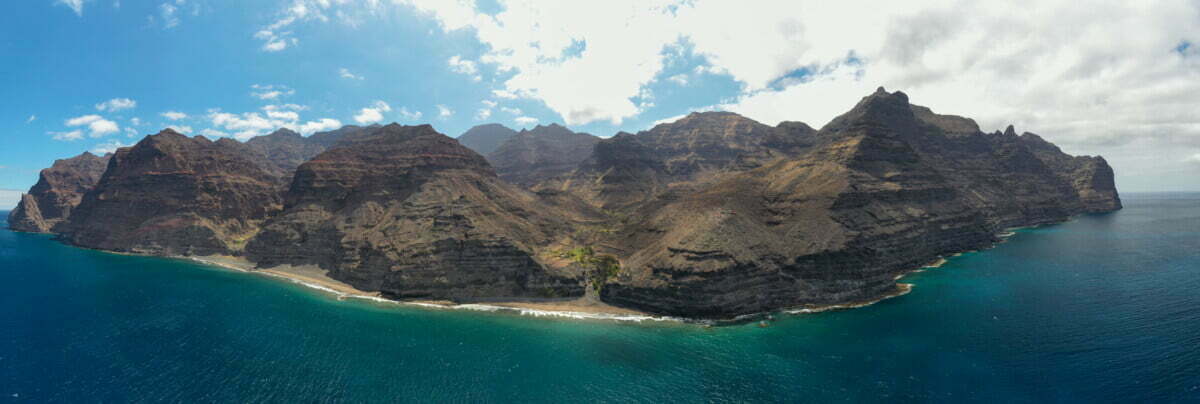
The Cabildo de Gran Canaria island government has acquired, through auction from the State Tax Administration Agency (AEAT), a total of 2,852,630 square meters, in two plots, at the centre of the Güigüí Grande and Chico ravines, for €2,876,000. These lands join the 225,340 m2 purchased via the same procedure last January, for a total of 3,071,000 square meters, making the land public property.
 In the two purchase projects the institution spent a total of €3.1 million, representing just 7.5% of the price requested at the time by the former owners, and one and a half million euros less than the appraisal that was carried out 13 years ago commissioned by the Cabildo. Between the Cabildo owned land and local government municipal property, the majority of the accesible areas of the Güi-Güí Special Natural Reserve now becomes publicly owned, leaving several inaccessible areas and cliffs in private hands.
In the two purchase projects the institution spent a total of €3.1 million, representing just 7.5% of the price requested at the time by the former owners, and one and a half million euros less than the appraisal that was carried out 13 years ago commissioned by the Cabildo. Between the Cabildo owned land and local government municipal property, the majority of the accesible areas of the Güi-Güí Special Natural Reserve now becomes publicly owned, leaving several inaccessible areas and cliffs in private hands.
The president of the Cabildo de Gran Canaria, Antonio Morales, explained in a visit this week, accompanied by technicians, representatives of the Tax Agency and journalists, just off shore from this spectacular wild part of Gran Canaria’s West Coast, that “Güi-Güí is part of our identity, as a landscape, as a symbol of the island, as [our] cultural and natural heritage” and the purchase of these plots is now a historical fact that brings to a close “a long struggle to guarantee protection for one of the places with the greatest natural and historical wealth on the island, which becomes everyone’s on Gran Canaria”.
 The purchase was part of a strategic policy from the Cabildo de Gran Canaria to acquire land of special ecological and patrimonial value as a way to guarantee its conservation and protection. This operation will allow the organising of how the areas is used within the reserve, since the farmlands are located in the ‘heart’ of Güi-Güí, and used often by the Canarian population, in the surroundings of the natural beaches and old farming areas.
The purchase was part of a strategic policy from the Cabildo de Gran Canaria to acquire land of special ecological and patrimonial value as a way to guarantee its conservation and protection. This operation will allow the organising of how the areas is used within the reserve, since the farmlands are located in the ‘heart’ of Güi-Güí, and used often by the Canarian population, in the surroundings of the natural beaches and old farming areas.
Güi-Güí, has three ecosystems in the same area, from pine forest, to thermophilic forest to the south and one of the most important cardonal-tabaibal enclaves in the world. Its environmental value exceeds the other national parks around the islands in the number of endemic species of flora, insects, reptiles, birds and marine fauna.
The “Montaña de los Cedros” is home to the only wild specimens of Canarian cedar on Gran Canaria, a population that has gone from just about 50 known specimens in 2003 to around 1,000 today, thanks to the Life Güi-Güí program that the Cabildo has been running since 2013, with funding from the European Union. The cedars are the last of the original forests that once populated this area, which were depleted by logging, and can now be regenerated in a natural way.
For all these reasons, Güi-Güí is a Special Natural Reserve, one of the largest existing protection categories, as well as a Special Conservation Area within the Natura 2000 network. It is also part of the nucleus of the Bisofera Reserve of Gran Canaria and its coast conserves one of Gran Canaria’s two major sebadales, natural seagrass meadows, declared a Marine Reserve and Natural Eco System of National Interest.
Archaeological Teams have cataloged 18 sites within the Güi-Güí massif, including mines (one of them the largest obsidian quarry on the island) and/or sanctuaries like the Hogarzales mountain and Los Cedros. In addition, the area, due to its isolation, has meant little of the land has been in use and few people have settled there. Güi-Güí is inaccessible to road traffic, which is unusual on an island so densely populated, offering a landscape very similar to how the island would have looked several centuries ago.